Battery Management Products
Battery charging
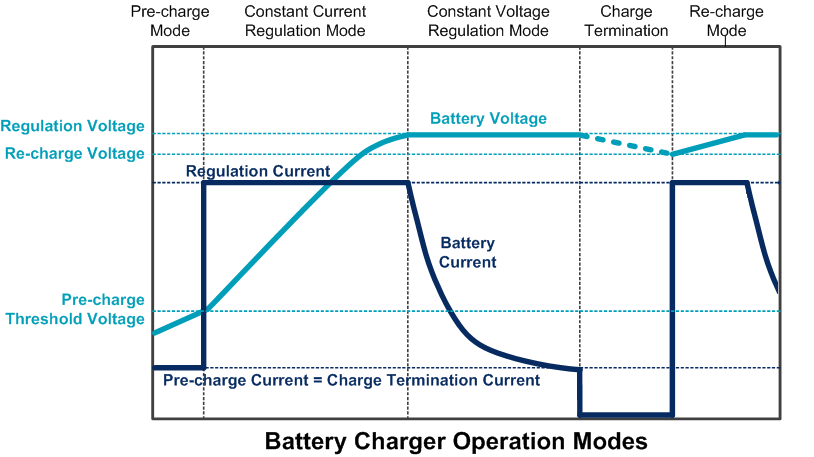
Charging Li-Ion cells needs special care, as overcharge can lead to unsafe conditions. Most Li-Ion chargers have pre-conditioning - constant current - constant voltage - current cut-off functionality as shown in Figure 1.
The charger maximum regulation voltage needs to be accurately controlled. In case of deep discharge, the battery charger will first provide a low pre-charge current, to pre-condition the battery for normal charging. This low preconditioning current can also reset the battery internal under-voltage protection.
During the constant current mode, the battery is charged with a defined current. When the battery voltage comes close to the regulation voltage (4.2V or 4.35V depending on battery type), the charge current drops gradually and the charger will work in constant voltage mode. This maximum regulation voltage needs to be accurately controlled to avoid over-charging which would damage the battery and result in unsafe conditions.
The battery is considered fully charged when the battery voltage is at its regulation voltage and charging current is less than a user defined percentage of rated charge current and charging is terminated. It is not recommended to continuously trickle charge Li-Ion cells, as this will reduce battery life. Most chargers will start a re-charge cycle when the battery voltage drops below a certain level (usually 0.1 ~ 0.2V below the regulation voltage).
When Li-Ion batteries are not used for a prolonged time period, it is better to discharge them to around 40% (~3.7V) to reduce their aging effect.
Battery temperature during charging needs to be monitored and too high or too low battery temperature should stop the charging process. For most Li-Ion batteries, normal charging conditions can be applied within the 10°C ~ 45°C temperature range. Charging should be cut-off when battery temperature is below 0°C or above 60°C.
Selected battery management components
Richtek has a wide range of Li-Ion chargers from linear to switching types. Linear charger topology is often used with batteries up to 1000mAh, while switching chargers are used for larger capacity batteries which can be charged with higher currents (>1A), or when using adapters with higher output voltage.
Linear Charger
Switching Charger
Up to 4A high current chargers
Up to 30V wide input chargers
Learn More