1 Key Features of Protection Switches
Featuring low forward voltage, programmable soft-start, start-up short-circuit protection, and robust fault protection mechanisms, the RT1985/RT1986/RT1987/RT1988 family simplifies power path management while increasing system reliability. Compared to discrete MOSFET implementations, this family offers a smaller footprint, easier design integration, and superior protection features.
|
Product
|
Operation Vin
|
Maximum Continuous Current
|
OVP Threshold
|
Package
|
|
RT1985
|
3.4V to 23V
|
8A
|
Fixed
|
VDFN-12TL 3x3
|
|
RT1986
|
3.4V to 23V
|
5.5A
|
Fixed
|
VDFN-12TL 3x3
|
|
RT1987
|
3.4V to 32V
|
8A
|
Programmable
|
VDFN-12T1L 3x3
|
|
RT1988
|
3.4V to 53V
|
8A
|
Programmable
|
VDFN-20TL 5.2x4
|
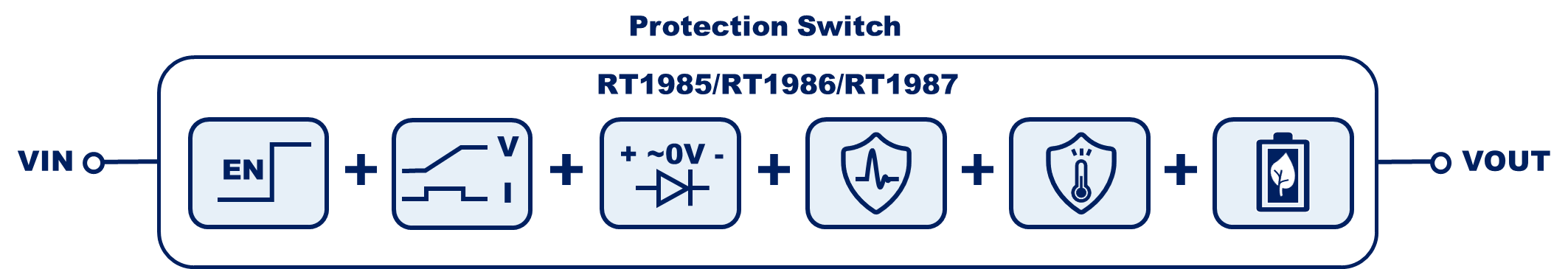
Figure 1. Protection Switch Features
1.1 Power Control (On/Off Switching)
Protection switches provide a straightforward method to control the connection and disconnection of power to specific loads without mechanical relays. This allows for better power sequencing and dynamic power management. The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 provides precise power path control through an active-high EN pin. When EN is asserted high and the input voltage exceeds the UVLO threshold, the power path is enabled with a defined delay and controlled ramp-up behavior.
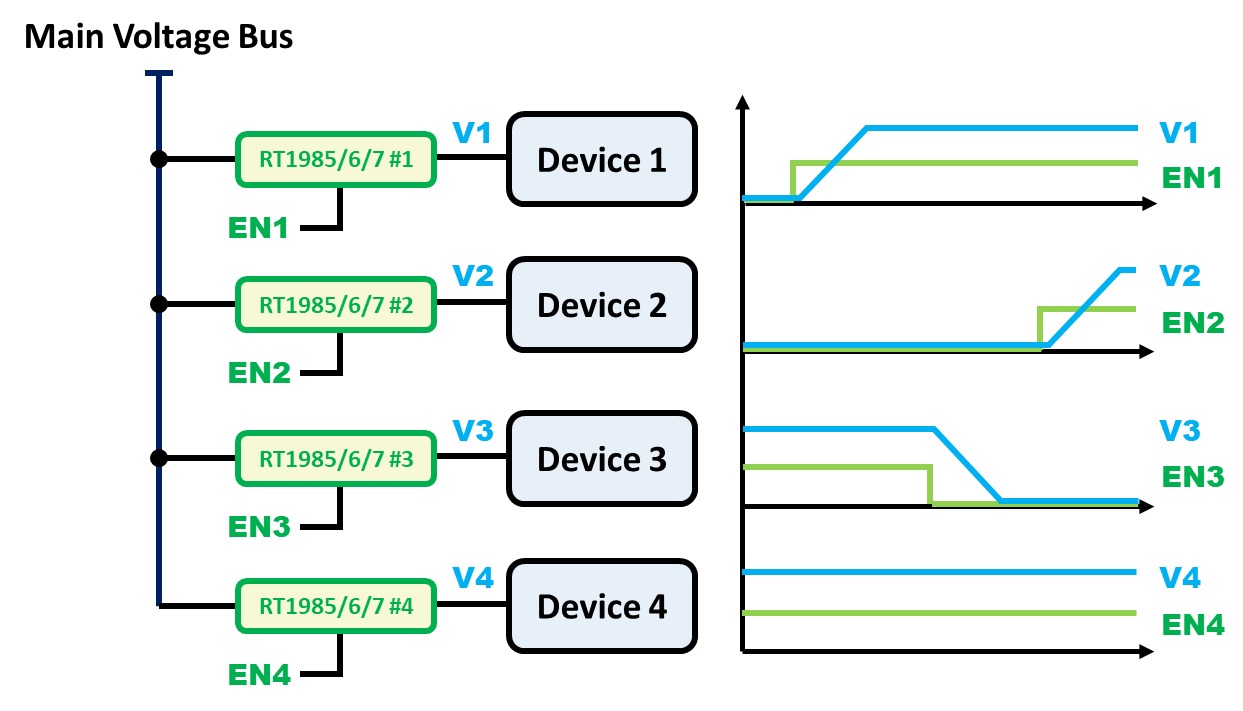
Figure 2. Enable Control of the Protection Switch
1.2 Programmable Soft-Start and Inrush Current Control
Many protection switches incorporate built-in soft-start features by controlling the gate drive voltage, allowing a gradual increase in output voltage and current. The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 includes an adjustable soft-start feature. By adjusting an external soft-start capacitor, designers can set the VOUT slew rate and limit the inrush current. This prevents voltage glitches on the main bus, protecting sensitive devices that share the same supply. This feature is critical for systems with large capacitance. Refer to the datasheet for detailed soft-start capacitor design guidelines.
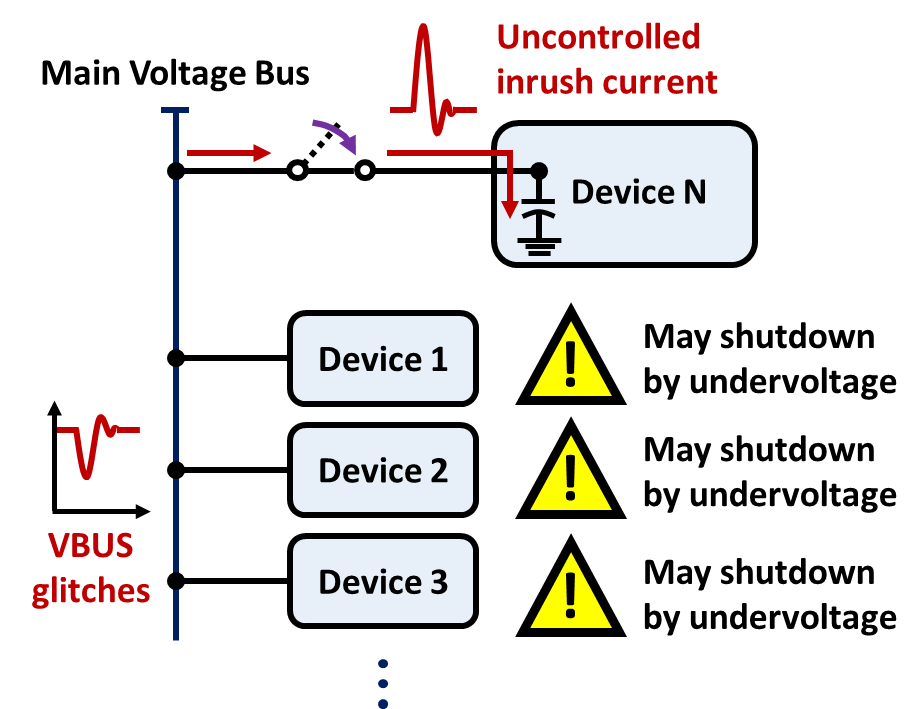
Figure 3. Startup without the Inrush Current Control
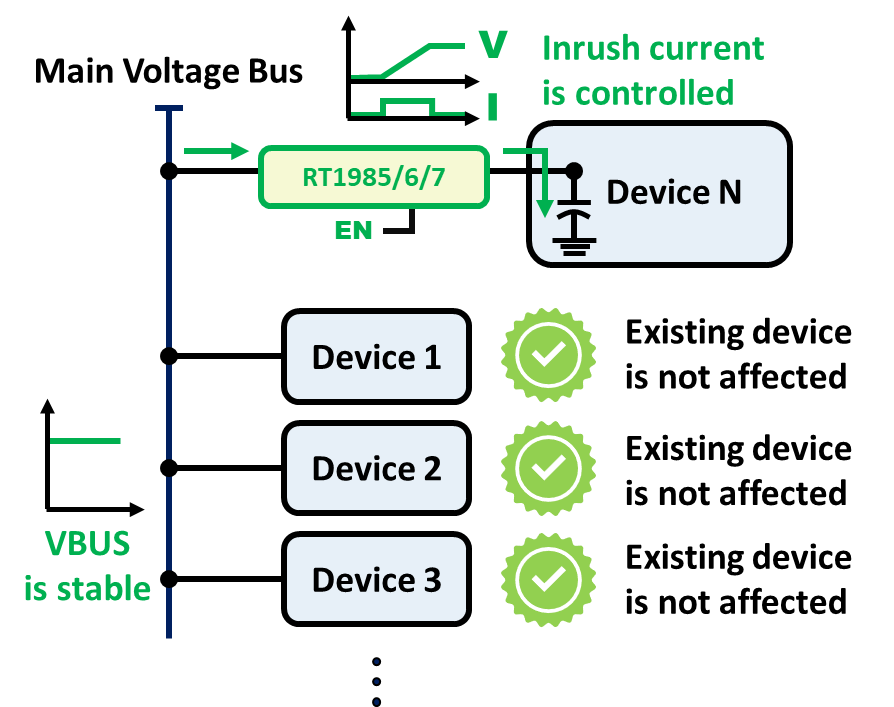
Figure 4. Startup with the Inrush Current Control
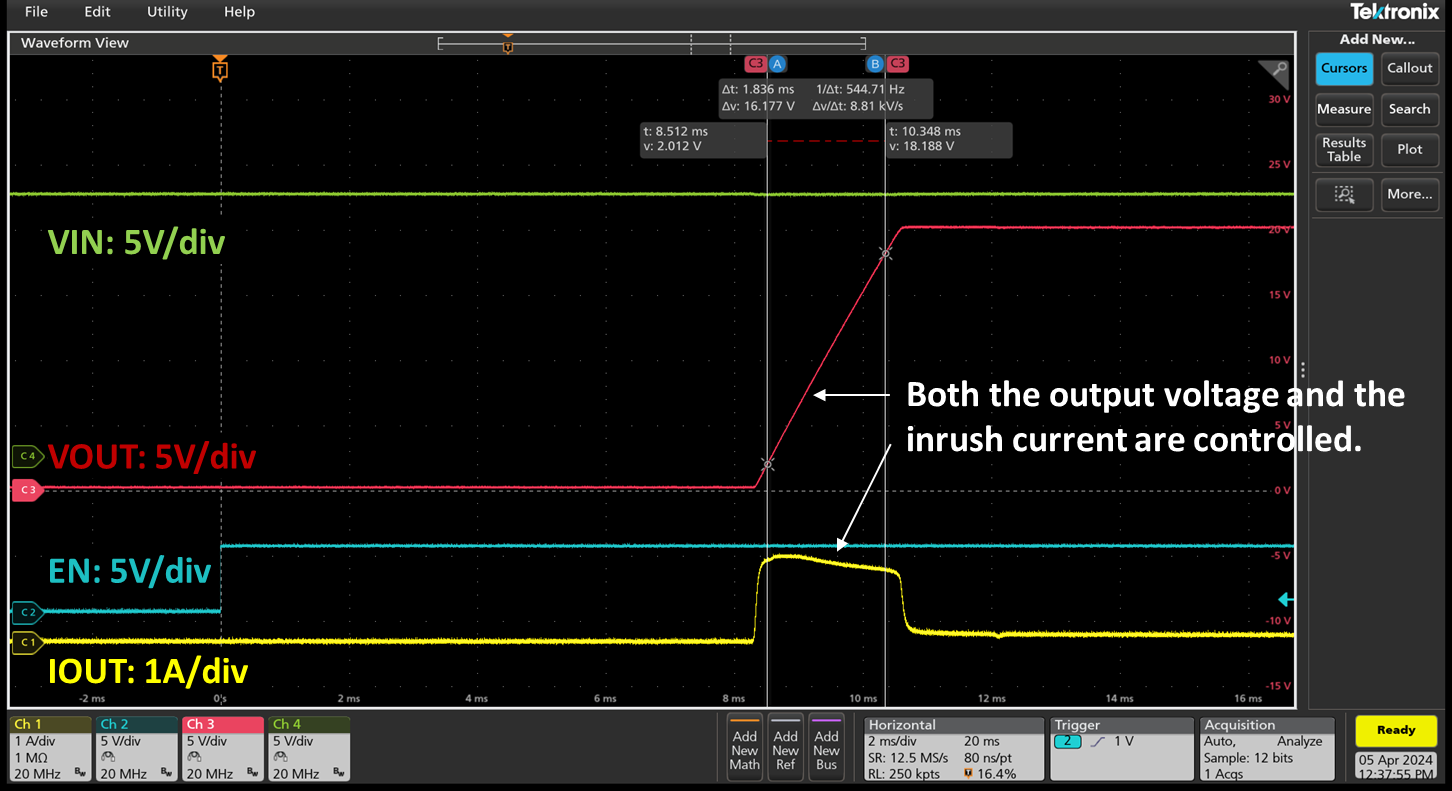
Figure 5. RT1985 Soft-Start Test Results
1.3 Start-Up Short-Circuit Protection (SCP)
During startup, the RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 monitors the output current. If an excessive inrush current or a hard short is detected, the device safely shuts down and retries after a defined delay, ensuring robust protection even under fault conditions.
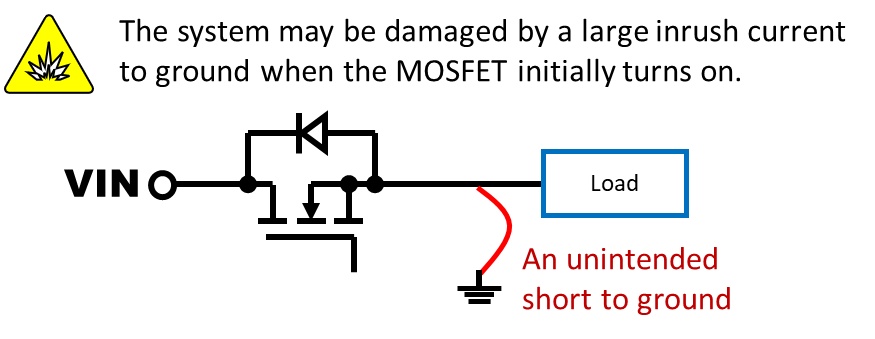
Figure 6. A MOSFET is used as a protection switch
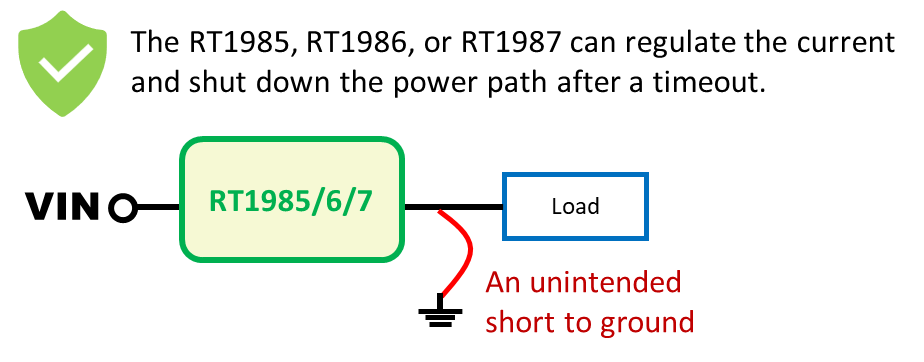
Figure 7. The RT1985/RT1986/RT1987/RT1988 is used as a protection switch
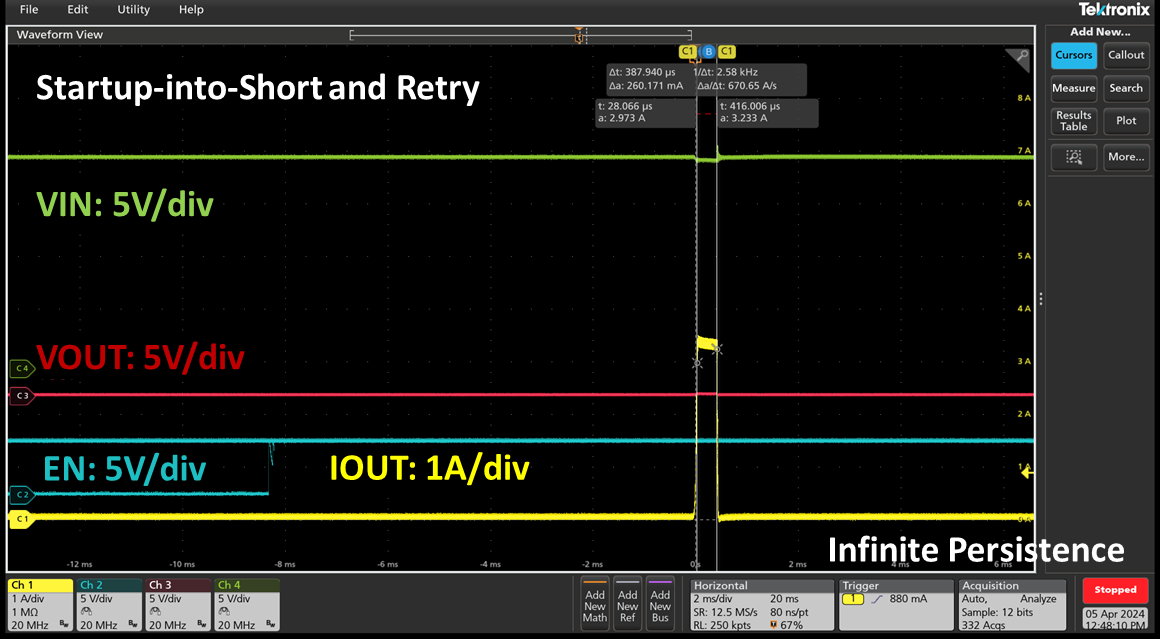
Figure 8. RT1985 Startup-into-Short and Retry Test Results
1.4 Reverse Current Blocking
Some protection switches offer reverse current blocking to prevent current from flowing backward from the output to the input, which is especially important in redundant power source systems. The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 offers Ideal Diode True Reverse Current Blocking (TRCB) capability, regulating the forward voltage drop and preventing reverse current flow from VOUT to VIN. This is essential in ORing applications where multiple power sources share a common load.
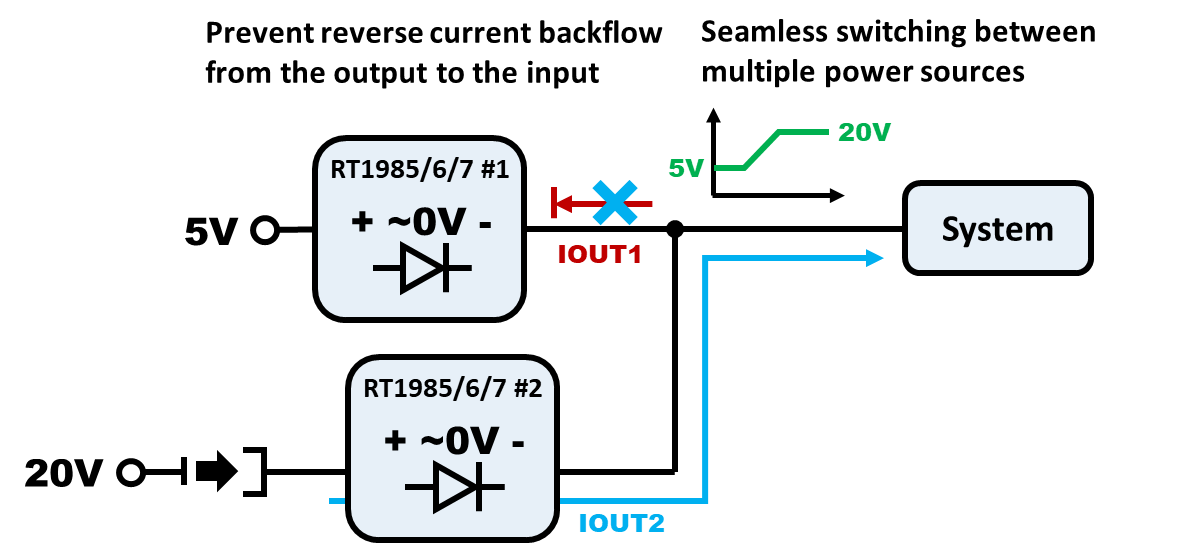
Figure 9. Reverse Blocking from the Output to the Input
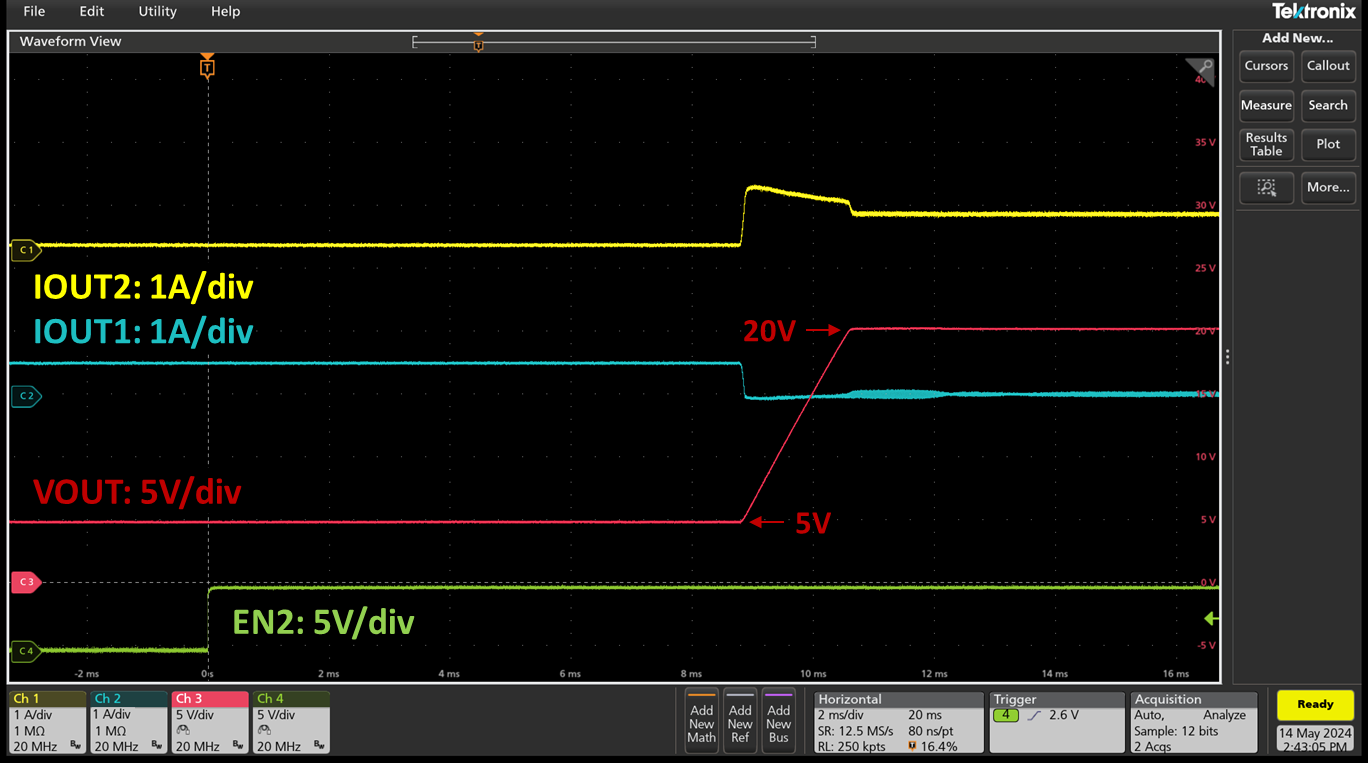
Figure 10. RT1985 Reverse Blocking Protection Test Results
1.5 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
Some protection switches integrate overvoltage protection to safeguard downstream circuitry from input voltage spikes or abnormal conditions. The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 includes OVP functionality that disconnects the load when the input voltage exceeds a defined threshold, preventing damage to sensitive components. This feature is particularly valuable in USB-C and power ORing systems, where unpredictable input sources may expose the system to voltage surges.
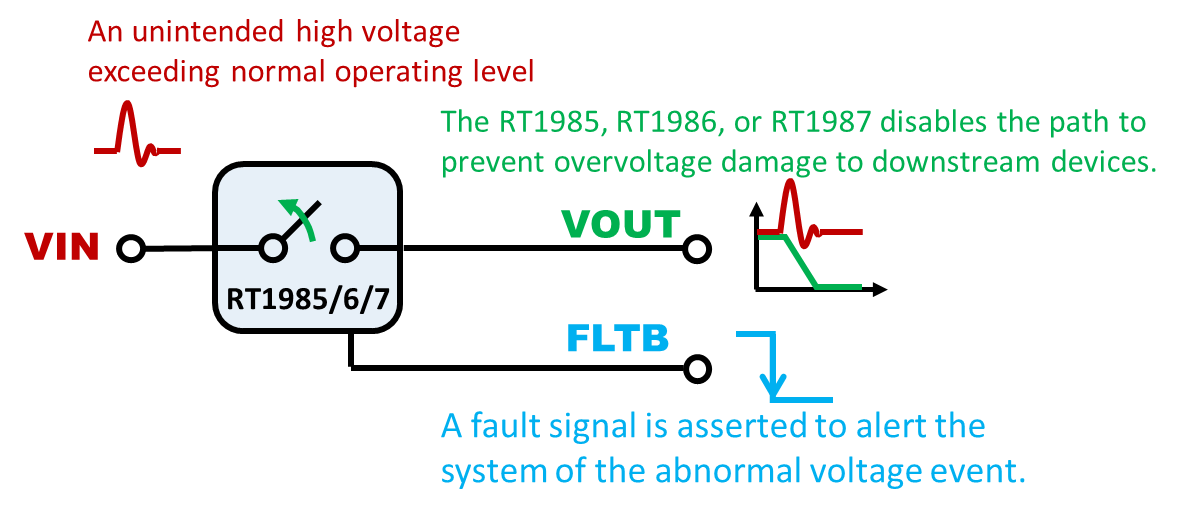
Figure 11. Overvoltage Protection from Excessive Input Voltage
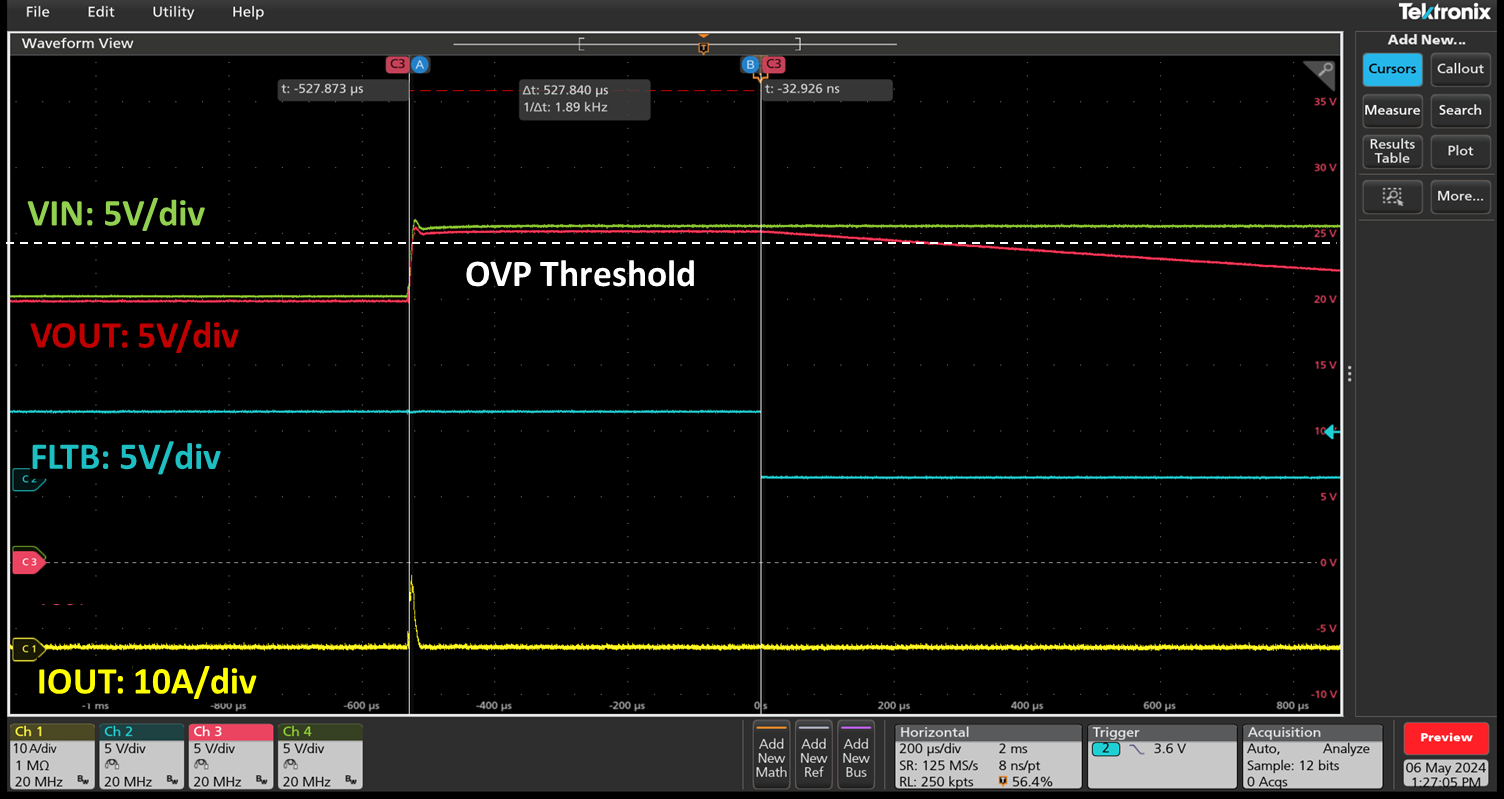
Figure 12. RT1985 Overvoltage Protection Test Results
1.6 Over-Temperature Protection
Advanced protection switches integrate thermal protection mechanisms. If the device's junction temperature exceeds a critical threshold, it automatically turns off to prevent permanent damage. The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 actively monitors the die temperature. If an excessive temperature (~140°C) is detected, the device disconnects the load and asserts a fault indication, enhancing system safety.
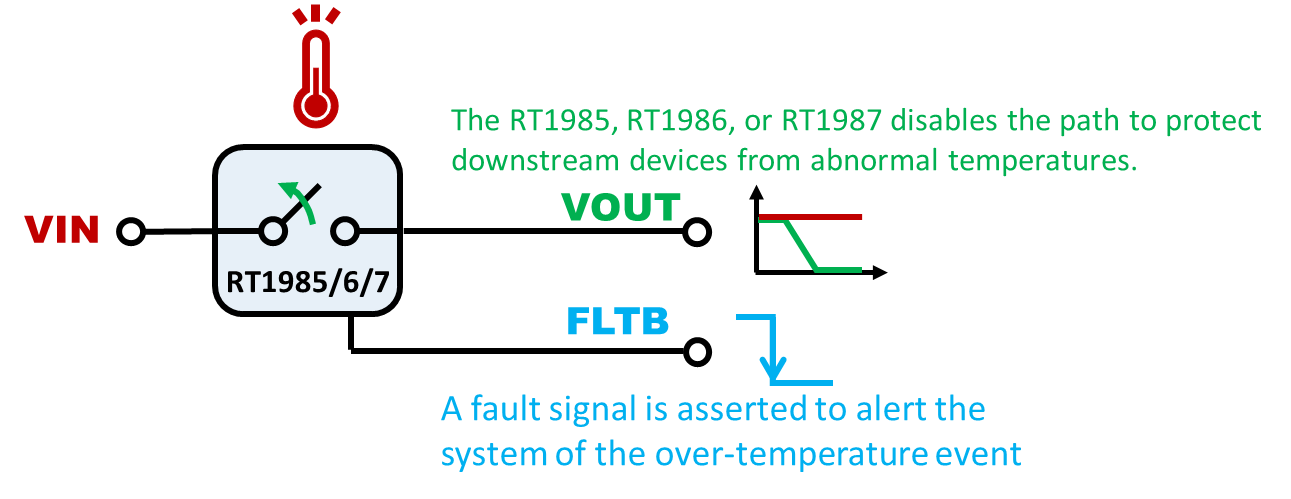
Figure 13. Over-Temperature Protection from Abnormal Thermal Conditions
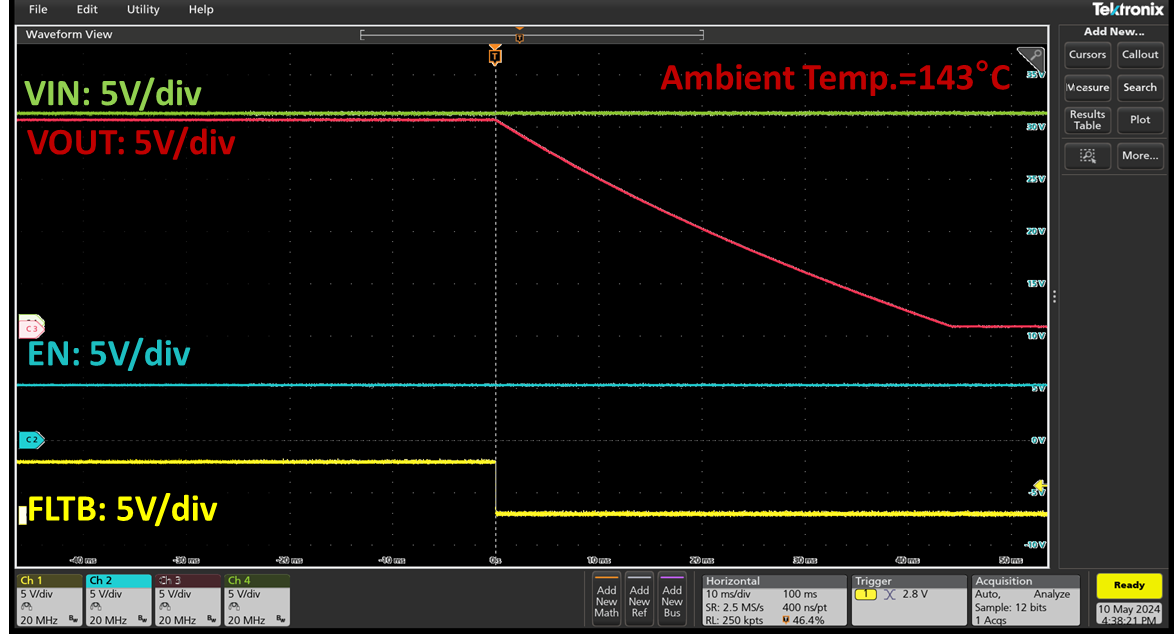
Figure 14. RT1985 Over-Temperature Protection Test Results
1.7 Low On-Resistance (20mΩ)
The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 adopts advanced process technology to reduce the on-resistance (RON) of the internal MOSFET to as low as 20mΩ, effectively minimizing power loss during high current transmission (P = I²R). This not only reduces device heating but also improves overall thermal efficiency.
1.8 Ultra-Low Quiescent Current
The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 features an ultra-low quiescent current design, meaning that the IC itself consumes minimal power under no-load or light-load conditions. This further optimizes overall system power consumption and extends battery life, making it well-suited for portable devices such as laptops and tablets.
2 Application Examples
2.1 USB-C/Thunderbolt Power Delivery
Protection switches are critical in USB-C and Thunderbolt applications, where they control and protect power delivery to devices. They ensure safe connection and disconnection during dynamic power negotiation processes, managing inrush currents, and preventing backflow. Figure 15 illustrates the RT1985 used for sink and source control in a dual-port USB PD application.
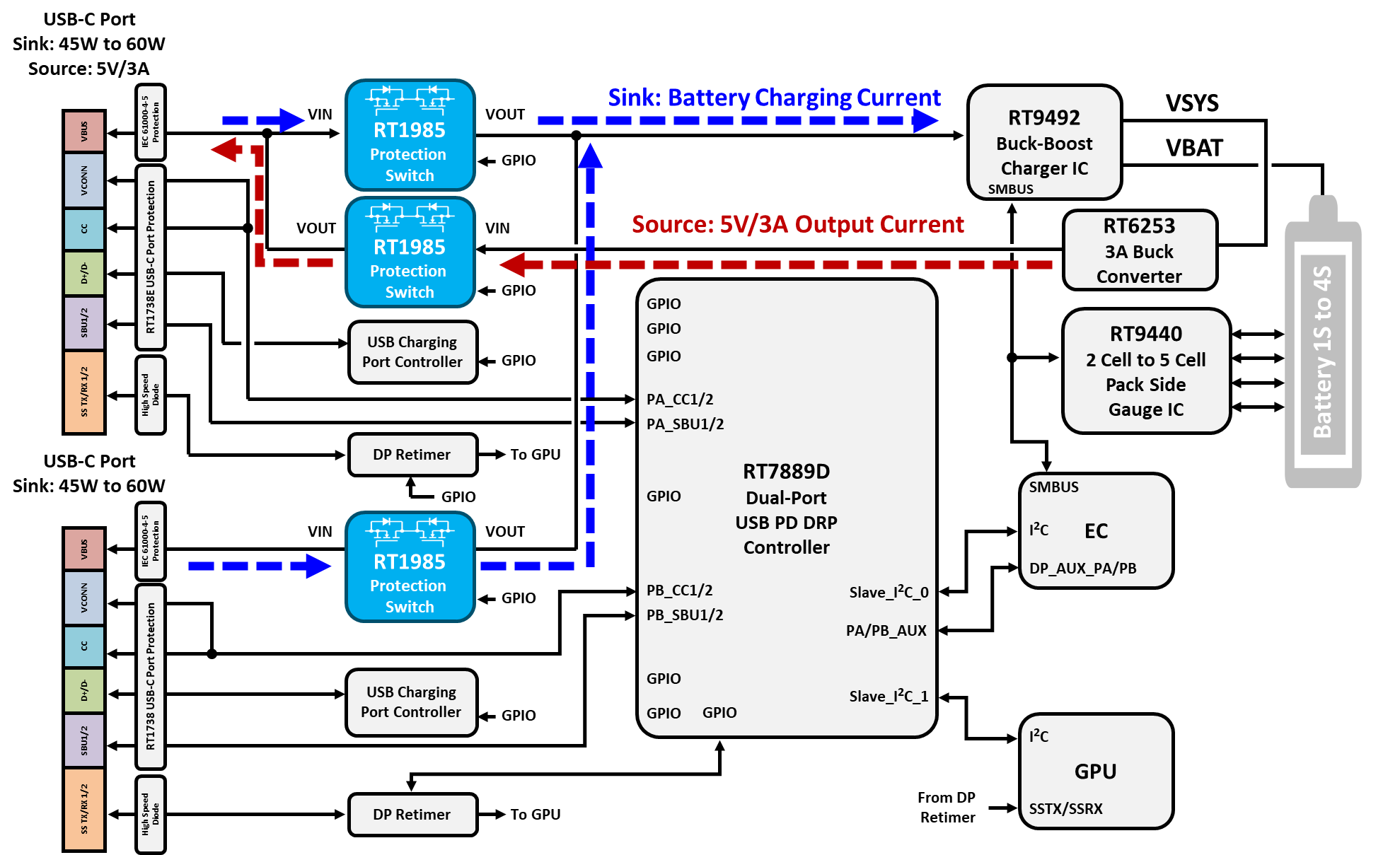
Figure 15. RT1985 for Sink and Source Control in a Dual-Port USB PD Application
Note 1. The above system diagram is for reference only. Actual products should be evaluated and adjusted based on your specific application requirements. For further assistance, please contact our regional office.
2.2 Docking Stations
In docking stations for laptops and tablets, protection switches are used to selectively enable or disable power to various ports and peripherals, helping optimize overall system efficiency, minimize standby power losses, and provide fault isolation.
2.3 Power ORing Applications
Protection switches with true reverse current blocking capability enable reliable power ORing. This allows seamless switching between multiple power sources (such as adapters, batteries, or auxiliary supplies) without backfeeding, ensuring system continuity and reliability.
3 Conclusion
Proper integration of protection switches enhances system reliability, reduces design complexity, and optimizes energy efficiency. As systems become increasingly complex, protection switches will continue to play a vital role in intelligent power distribution strategies. The RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 offers a highly integrated and robust solution for power path control, featuring Ideal Diode reverse current blocking, programmable soft-start, and advanced fault protection. Its compact design and versatile protection features make it ideal for demanding applications such as USB-C sink power delivery, docking stations, and power ORing systems. Leveraging the RT1985, RT1986, RT1987 or RT1988 simplifies power management design, increases system reliability, and enhances the end-user experience in next-generation electronic products.
To stay informed with more information about our products, please subscribe to our newsletter.